Introduction to the rpact Package
November 13, 2025
Overview 📦
- Comprehensive validated R package implementing methodology described in Wassmer and Brannath (2016), second edition published in Sep. 2025
- Enables the design of traditional and confirmatory adaptive group sequential designs
- Provides interim data analysis and simulation including early efficacy stopping and futility analyses
- Enables sample-size reassessment with different strategies
- Enables treatment arm selection in multi-stage multi-arm (MAMS) designs
- Enables subset selection in population enrichment designs
- Provides a comprehensive and reliable sample size calculator

Developed by RPACT 🏢
- RPACT company founded in 2017 by Gernot Wassmer and Friedrich Pahlke
- Idea: open source development with help of “crowd funding”
- Currently supported by 21 companies
- \(>\) 80 presentations and training courses since 2018, e.g., FDA in March 2022
- 29 vignettes based on Quarto and published on rpact.org/vignettes
- 28 releases on CRAN since 2018



RCONIS 🚀
- Grow RPACT company to offer a wider range of services
- Statistical consulting and engineering services: Research Consulting and Innovative Solutions
- Joint venture between RPACT GbR (rpact.com) and inferential.biostatistics GmbH (inferential.bio) founded by Daniel Sabanés Bové and Carrie Li
- Website: rconis.com

The R Package rpact – Functional Range

Trial Designs 🔬
- Fixed sample designs:
- continuous, binary, count, survival outcomes
- Group sequential designs:
- efficacy interim analyses, futility stopping, alpha-spending functions
- Adaptive designs:
- Inverse normal and Fisher’s combination test, conditional error rate principle
- Provides adjusted confidence intervals and bias corrected estimates
- Multi-arm multi-stage (MAMS) and enrichment designs, sample size reassessment
Sample Size and Power Calculation 💻
Sample size and power can be calculated for testing:
- means (continuous endpoint)
- proportions (binary endpoint)
- hazards (survival endpoint)
- Note: flexible recruitment and survival time options
- rates (count endpoint)
Example: Sample Size Calculation 🧮
Sample size calculation for a continuous endpoint
Sequential analysis with a maximum of 3 looks (group sequential design), one-sided overall significance level 2.5%, power 80%. The results were calculated for a two-sample t-test, H0: mu(1) - mu(2) = 0, H1: effect = 2, standard deviation = 5.
| Stage | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planned information rate | 33.3% | 66.7% | 100% |
| Cumulative alpha spent | 0.0001 | 0.0060 | 0.0250 |
| Stage levels (one-sided) | 0.0001 | 0.0060 | 0.0231 |
| Efficacy boundary (z-value scale) | 3.710 | 2.511 | 1.993 |
| Futility boundary (z-value scale) | 0 | 0 | |
| Efficacy boundary (t) | 4.690 | 2.152 | 1.384 |
| Futility boundary (t) | 0 | 0 | |
| Cumulative power | 0.0204 | 0.4371 | 0.8000 |
| Number of subjects | 69.9 | 139.9 | 209.8 |
| Expected number of subjects under H1 | 170.9 | ||
| Overall exit probability (under H0) | 0.5001 | 0.1309 | |
| Overall exit probability (under H1) | 0.0684 | 0.4202 | |
| Exit probability for efficacy (under H0) | 0.0001 | 0.0059 | |
| Exit probability for efficacy (under H1) | 0.0204 | 0.4167 | |
| Exit probability for futility (under H0) | 0.5000 | 0.1250 | |
| Exit probability for futility (under H1) | 0.0480 | 0.0035 |
Legend:
- (t): treatment effect scale
Adaptive Analysis 📈
Perform interim and final analyses during the trial using group sequential method or p-value combination test (inverse normal or Fisher)
Calculate adjusted point estimates and confidence intervals (cf., Robertson et al. (2023), Robertson et al. (2025))
Perform sample size reassessment based on the observed data, based on calculation of conditional power
Some highlights:
- Automatic boundary recalculations during the trial for analysis with alpha spending approach, including under- and over-running
- Adaptive analysis tools for multi-arm trials and enrichment designs
Simulation Tool 🧪
Obtain operating characteristics of different designs:
- Assessment of adaptive sample size recalculation strategies
- Assessment of treatment selection strategies in multi-arm trials
- Assessment of population selection strategies in enrichment designs
Easy to understand R commands:
Example:
\(\rightarrow\) rpact useful for conducting flexible simulations in clinical trial planning
User Concept – R generics
In general, everything runs with the R standard functions which are always present in R: R generics.
- Visualize:
print()summary()plot()
- Continue work:
as.data.frame()length()names()
User Concept – Most parameters have a default value
Example: getDesignInverseNormal() produces the output:
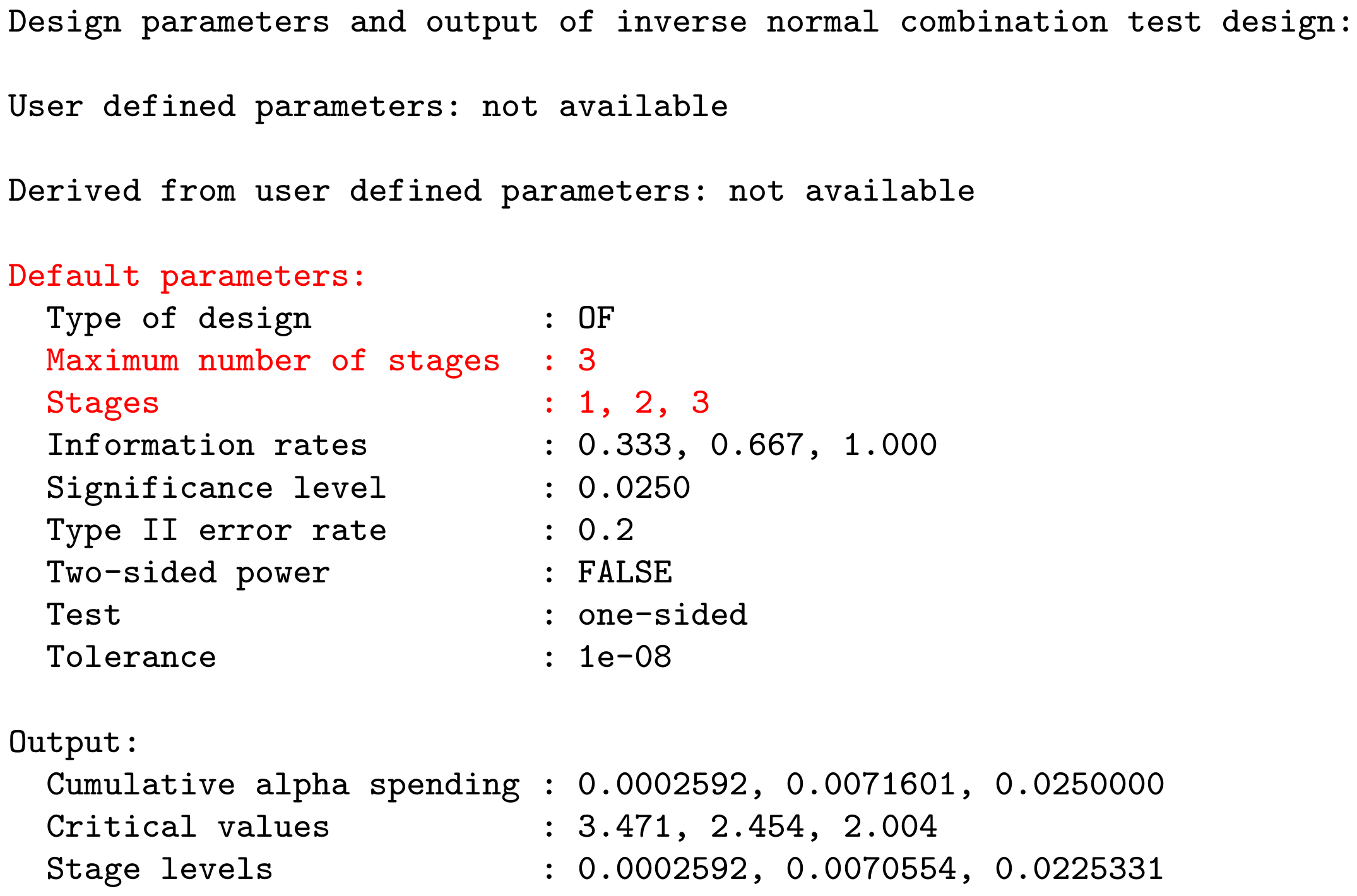
User Concept – Most parameters have a default value
Example: getDesignInverseNormal(kMax = 2) produces the output:
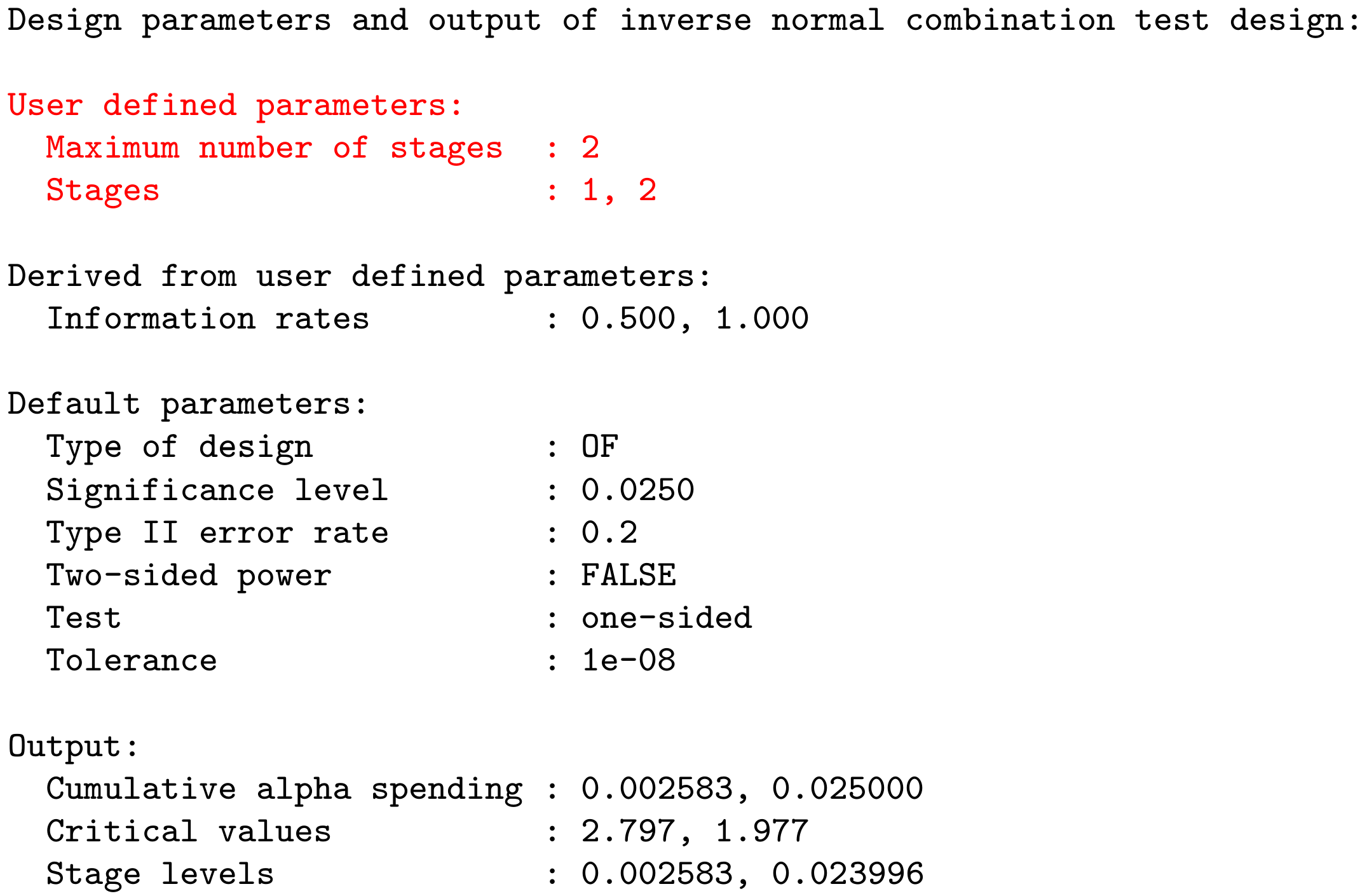
Recent Developments
Just in the near future you will see in rpact:
- Patient level survival data simulations for multi-arm and enrichment designs
- Optimum conditional error functions according to Brannath et al. (2024) (package optconerrf published on CRAN Sep 09, 2025)
- Least square means interface for continuous endpoints
- Additional futility boundary scales: function
getFutilityBounds()- Available scales: zValue, pValue, conditionalPower, condPowerAtObserved, predictivePower, reverseCondPower, effectEstimate (cf., Ortega-Villa et al. (2025))
Second Edition of the Book

- Group Sequential and Confirmatory Adaptive Designs in Clinical Trials by Gernot Wassmer and Werner Brannath
- Second Edition (Springer, 2025) — published on September 24, 2025
- Now featuring numerous rpact R code examples demonstrating the methods implemented in the package
- For more information, visit: link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-031-89669-9
The R Package rpact – Getting started
Various learning concepts available:
- Training, online or onsite: www.rpact.com/contact
- Vignettes: www.rpact.org/vignettes
- Graphical user interface RPACT Cloud: cloud.rpact.com
